Detailed Design
Component Design
The component design of Poolerz.
The diagrams below provide a detailed breakdown of our application’s static and dynamic architectures, showcasing relationships, dependencies, method overviews, and system components.
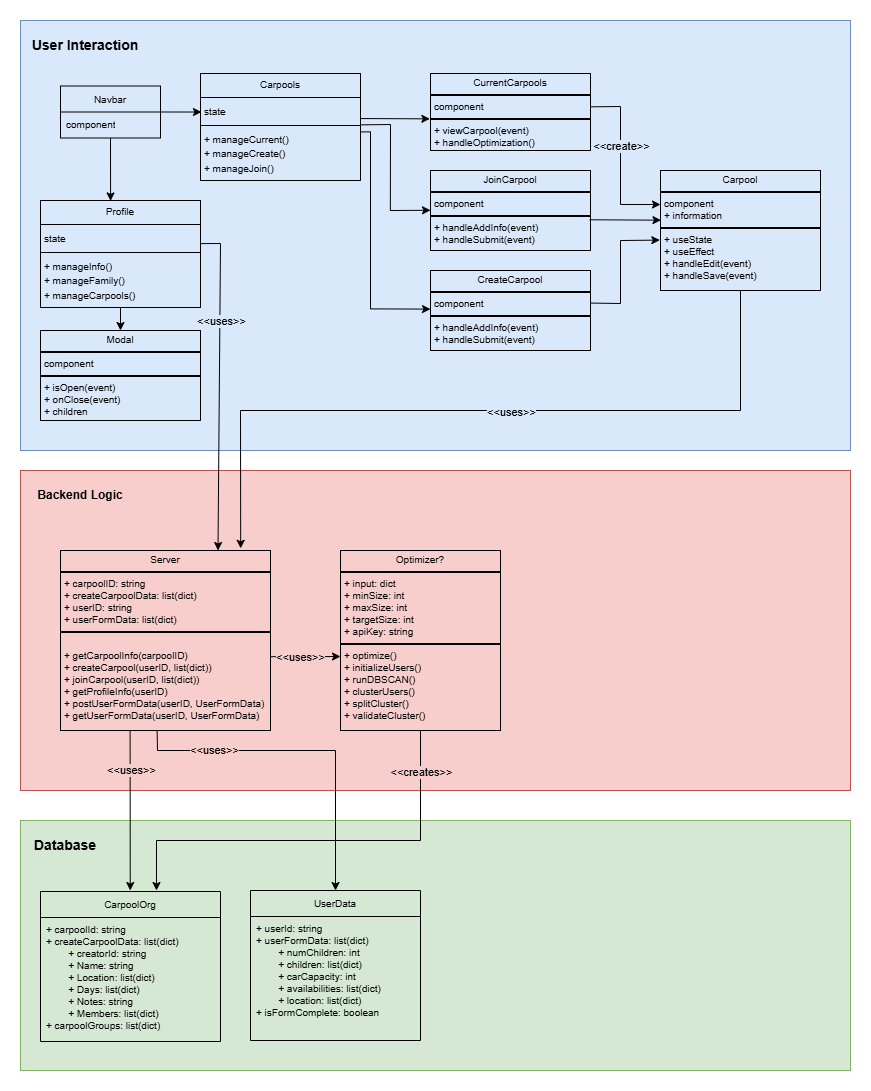 The static component diagram (Figure 3.1) outlines the key system elements and their interactions.
The static component diagram (Figure 3.1) outlines the key system elements and their interactions.
Instead of a traditional component diagram, we use a class diagram to clearly depict:
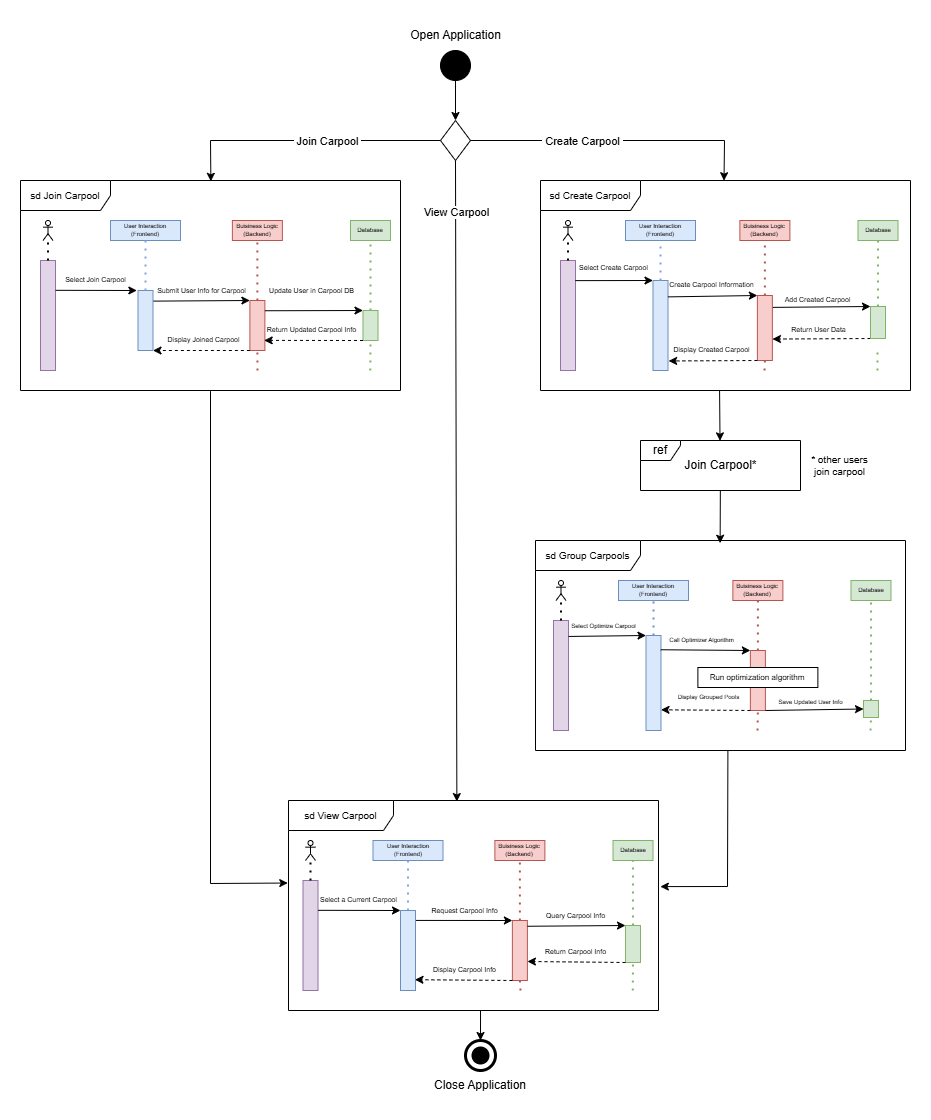 The dynamic architecture diagram (Figure 3.2) illustrates the user flow when:
The dynamic architecture diagram (Figure 3.2) illustrates the user flow when:
By integrating both static and dynamic architecture models, our design ensures:
- Static Architecture: Expands on the general system architecture (Figure 1) by breaking down the frontend, backend, and database layers, showing interactions during carpool creation and joining.
- Dynamic Architecture: Builds on the static architecture by demonstrating user interactions and response flows across layers.
Static Component Architecture
 The static component diagram (Figure 3.1) outlines the key system elements and their interactions.
The static component diagram (Figure 3.1) outlines the key system elements and their interactions.Instead of a traditional component diagram, we use a class diagram to clearly depict:
- Application elements
- Interactions across layers
Key Layers & Components
Frontend Layer
This layer consists of UI components that the user directly interacts with:- Profile
- Modal
- JoinCarpool
- CreateCarpool
- Displaying user interfaces
- Accepting user input
- Interacting with the backend for functional operations
<<uses>> and <<creates>> indicate dependencies between components.
Business Logic Layer
This layer includes:- Server & Optimizer: Handles data retrieval, user updates, and carpool grouping logic.
Database Layer
- The backend interacts with the database to update:
- Carpools Collection: Stores carpool details, schedules, and members.
- UserData Collection: Stores user profiles and personal details.
Dynamic Component Architecture
 The dynamic architecture diagram (Figure 3.2) illustrates the user flow when:
The dynamic architecture diagram (Figure 3.2) illustrates the user flow when:
- Joining a carpool
- Creating a carpool
- Viewing a carpool
- Primary user flows
- Multiple sequence diagrams nested within different processes
Key User Flows
1. Joining a Carpool
- User selects a carpool from the UI.
- Data is sent to the backend, where the system:
- Adds the user to the carpool database.
- Sends confirmation of successful join.
2. Creating a Carpool
- User inputs carpool details via the frontend.
- Backend processes the request and:
- Creates a new carpool entry in the database.
- Returns confirmation of creation to the frontend.
3. Viewing a Carpool
- User selects a carpool to view.
- Frontend requests carpool details from the backend.
- Backend queries the database and:
- Retrieves relevant data.
- Returns the information to be displayed on the UI.
By integrating both static and dynamic architecture models, our design ensures:
- Clear system structure
- Efficient data flow
- Scalability and maintainability

